Unlocking the Secrets of LC Circuit Phasor Diagrams
Ever wondered how electrical engineers make sense of the intricate dance of currents and voltages in circuits? One powerful tool they employ is the LC circuit phasor diagram. Think of it as a roadmap, visually mapping the relationship between voltage and current in a circuit containing an inductor (L) and a capacitor (C). These diagrams transform complex equations into easily digestible visuals, making circuit analysis much simpler.
LC circuits, at their core, are energy storage devices. The inductor stores energy in a magnetic field, while the capacitor stores it in an electric field. When connected together, these components create a resonant circuit, oscillating at a specific frequency. This oscillation is where the phasor diagram comes in, helping us visualize the phase difference between voltage and current.
The concept of phasor diagrams arose from the need to represent sinusoidal quantities, like AC voltage and current, in a more manageable way. Early electrical engineers struggled with complex number calculations, so they developed phasor representations as a graphical shortcut. This visualization technique revolutionized circuit analysis, particularly for AC circuits with inductors and capacitors, allowing for easier calculation of impedance, resonance, and other important parameters.
Understanding LC circuit behavior is crucial in numerous applications, from radio tuning to power factor correction. LC circuit phasor diagrams play a vital role in designing and analyzing these circuits. By visualizing the phase relationship and magnitudes of voltage and current, engineers can optimize circuit performance and predict behavior under different conditions. Without these diagrams, analyzing complex resonant circuits would be a significantly more challenging task.
A common challenge in working with LC circuits is understanding the concept of resonance. This occurs when the inductive reactance and capacitive reactance are equal, resulting in a purely resistive circuit. Phasor diagrams clearly illustrate this condition, showing the voltage and current in phase at resonance. However, deviations from resonance, due to component tolerances or frequency variations, can lead to unexpected circuit behavior. This is where the ability to interpret phasor diagrams becomes invaluable, allowing engineers to diagnose and troubleshoot circuit issues.
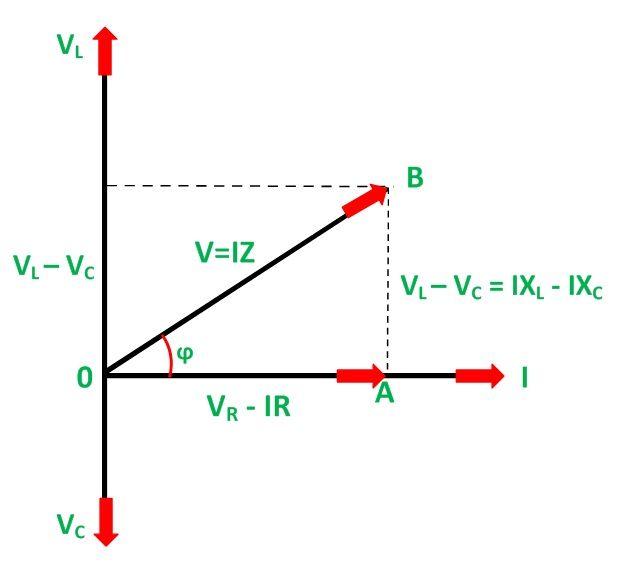
An LC circuit phasor diagram represents voltage and current as rotating vectors. The length of the vector represents the magnitude, and the angle represents the phase. For instance, in a purely inductive circuit, the current lags the voltage by 90 degrees, represented by the current phasor trailing the voltage phasor.
Benefits of using LC circuit phasor diagrams include: Simplified analysis of complex AC circuits, visualization of phase relationships between voltage and current, and easy determination of impedance and resonance conditions.
To construct an LC circuit phasor diagram, first, determine the reactance of the inductor and capacitor. Then, draw the voltage phasor as a reference. Finally, draw the current phasor based on the phase relationship determined by the circuit's impedance.
Advantages and Disadvantages of LC Circuit Phasor Diagrams
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Simplified visualization of complex AC circuits | Can be challenging to interpret for complex circuits with multiple components |
| Easy determination of phase relationships | Requires understanding of phasor representation and complex numbers |
| Facilitates calculation of impedance and resonance | Limited to steady-state analysis and does not represent transient behavior |
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What is a phasor? A phasor is a rotating vector representing a sinusoidal quantity.
2. What is an LC circuit? A circuit with an inductor and a capacitor.
3. What is resonance? When inductive and capacitive reactances are equal.
4. Why use a phasor diagram? Simplifies AC circuit analysis.
5. How do you draw a phasor diagram? Represent voltage and current as vectors.
6. What is impedance? The total opposition to current flow in an AC circuit.
7. What are the benefits of phasor diagrams? Simplified analysis and visualization.
8. What are the limitations of phasor diagrams? Limited to steady-state analysis.
Tips and tricks: Remember that the direction of rotation of phasors is conventionally counterclockwise. Practice drawing phasor diagrams for different LC circuit configurations to build proficiency.
In conclusion, LC circuit phasor diagrams are essential tools for electrical engineers and anyone working with AC circuits. They offer a powerful way to visualize and analyze the complex interactions between voltage, current, and impedance. While there might be a learning curve initially, mastering this technique opens doors to a deeper understanding of circuit behavior and simplifies the design and analysis process. By understanding the underlying principles and practicing with various examples, you can leverage the power of phasor diagrams to unlock the secrets of LC circuits and optimize their performance for a wide range of applications. So, dive in, explore, and let these diagrams guide you through the fascinating world of AC circuit analysis. Take the time to practice drawing and interpreting phasor diagrams, and you'll find them an invaluable asset in your electrical engineering toolkit.
Unlocking the fluff the ultimate guide to boy fluffy hair cuts
Free printable 30 day notice letter your ultimate guide
Level up your youtube presence crafting the perfect profile picture