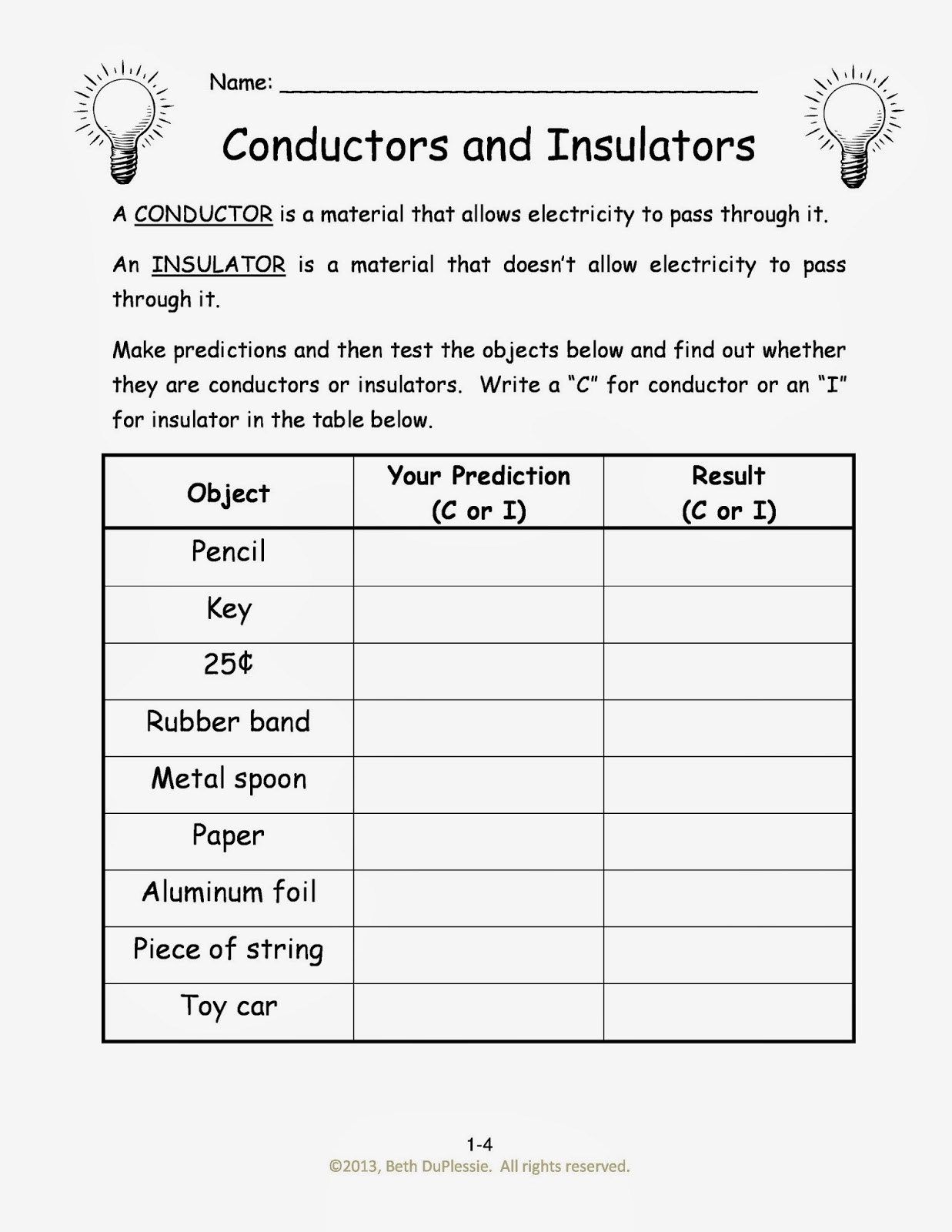
Unlocking the Power of Conductors and Insulators: A Visual Journey
Have you ever wondered how electricity flows through the wires in your house, or why the plastic coating around those wires keeps you safe? The answer lies in the fundamental difference between electrical conductors and insulators. Understanding these materials is crucial for grasping the basics of electricity and its safe application in our modern world. Conductors and insulators pictures provide a powerful visual tool for learning about these essential concepts, allowing us to see and understand their roles in various electrical systems.
Images of conductors and insulators offer a clear and concise way to distinguish between materials that readily allow electricity to flow and those that restrict its passage. Pictures of copper wires, aluminum foil, and other conductive materials help us visualize the free movement of electrons within their structure. Conversely, images of rubber gloves, plastic casings, and glass insulators demonstrate how these materials effectively block the flow of electrical current, protecting us from harm.
The historical development of our understanding of conductors and insulators is intertwined with the very discovery of electricity itself. Early experiments with static electricity and the subsequent invention of the Leyden jar led to the identification of materials that could either store or conduct electrical charges. These early observations laid the groundwork for the development of electrical circuits and the widespread use of electricity that we see today. Conductors and insulators pictures, particularly historical diagrams and illustrations, can offer a glimpse into the evolution of this crucial scientific understanding.
The importance of conductors and insulators in our modern society cannot be overstated. From the power grids that deliver electricity to our homes to the intricate circuitry within our smartphones, these materials are essential for the functioning of countless technologies. Pictures depicting these applications, such as power lines strung across vast distances or close-up views of circuit boards, highlight the ubiquitous presence and critical role of conductors and insulators in our everyday lives.
A key issue related to conductors and insulators pictures is the need for accurate and clear representation. Images should clearly differentiate between conductive and insulating materials, using appropriate labeling and visual cues. Misleading or inaccurate visuals can lead to misconceptions about electrical safety and the proper handling of electrical equipment. Therefore, it's crucial to use reliable sources for conductors and insulators pictures, ensuring that they accurately depict the properties and functions of these materials.
Simply put, electrical conductors are materials that allow electricity to flow easily through them. Common examples include metals like copper, silver, and aluminum. Insulators, on the other hand, are materials that resist the flow of electricity. Examples include rubber, plastic, glass, and wood.
Benefits of utilizing conductors and insulators pictures in educational materials or practical guides include: enhanced understanding through visualization, improved retention of information, and clearer communication of complex concepts. For example, a picture of a bird safely perched on a high-voltage power line, insulated from the current by its feet, vividly illustrates the principle of electrical insulation.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Pictures for Learning
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Improved understanding and retention | Potential for misinterpretation if images are unclear or inaccurate |
| Engaging and visually appealing learning experience | Limited ability to convey complex theoretical concepts without accompanying text |
| Easy to share and disseminate information | May not be accessible to all learners (e.g., visually impaired individuals) |
Real-world examples of conductors and insulators in action include: the copper wiring in our homes (conductor), the rubber coating around electrical cords (insulator), the ceramic insulators on power lines, the metal body of a car acting as a Faraday cage (conductor), and the plastic handles of cooking utensils (insulator).
Frequently asked questions about conductors and insulators include: What makes a material a good conductor? Why are insulators important for safety? How do semiconductors work? What is the difference between a conductor and a resistor? What are some common examples of conductors and insulators in everyday life? How can I test if a material is a conductor or insulator? What are the dangers of handling electrical conductors improperly? Where can I find reliable resources for conductor and insulator images?
In conclusion, understanding the difference between conductors and insulators is paramount for safely and effectively utilizing electricity. Conductors and insulators pictures are valuable tools for learning and visualizing these crucial concepts. By leveraging visual aids, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the role these materials play in our daily lives, from the power grids that illuminate our cities to the tiny circuits that power our devices. The responsible use and understanding of electricity rely on a clear understanding of conductors and insulators, making resources like conductor and insulator pictures essential for continued learning and innovation in this field.
The curious case of the vacuum cleaner vacuum cleaner
Unveiling the cosmos a guide to printable star charts
Al fateh sc a bahraini football powerhouse









:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/examples-of-electrical-conductors-and-insulators-608315_v3-5b609152c9e77c004f6e8892.png)