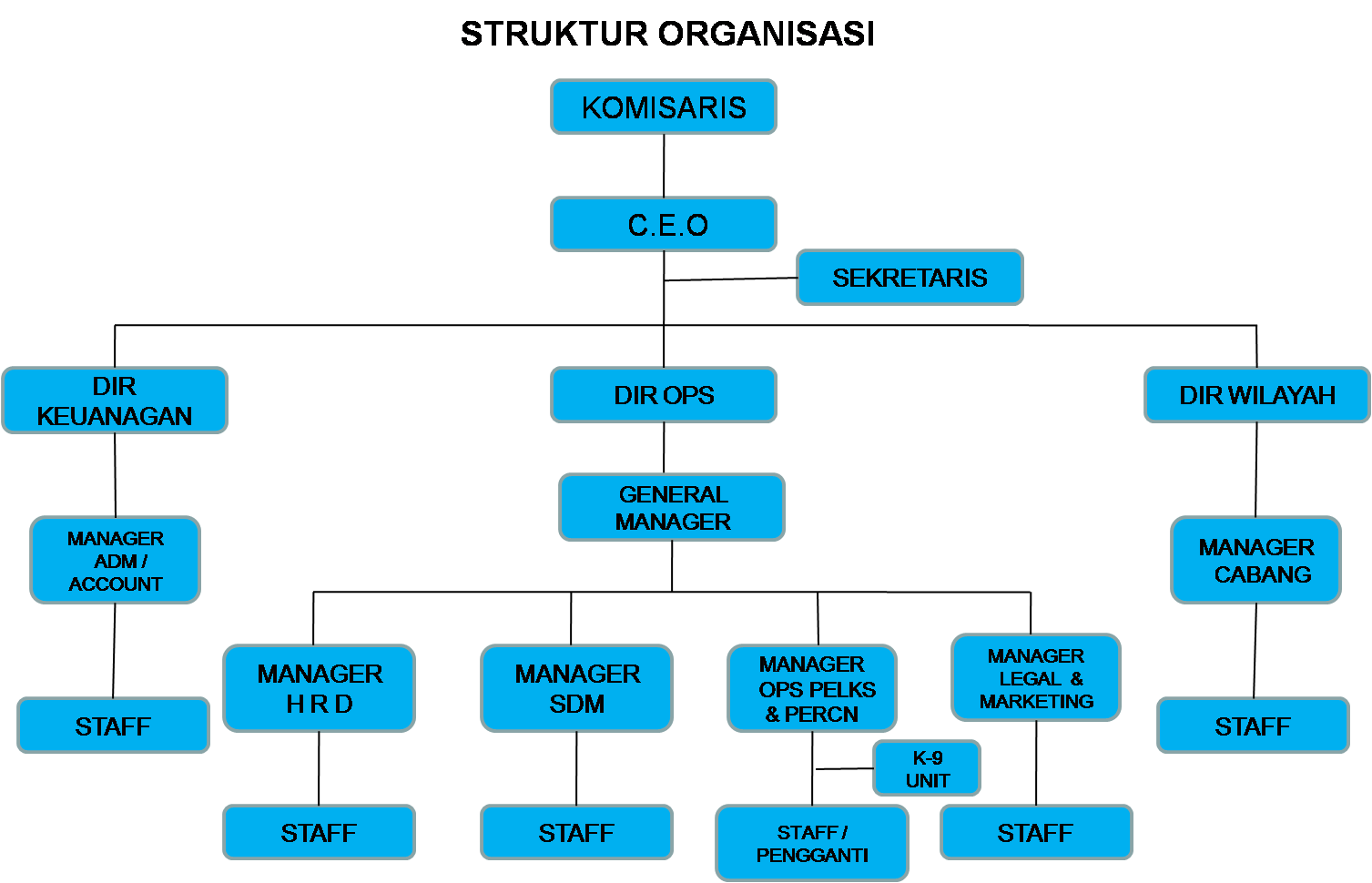
Unlocking Efficiency: Understanding Company Organizational Structure Levels
Imagine a bustling anthill – seemingly chaotic, yet remarkably organized. Each ant has a designated role, contributing to the colony's overall success. Similarly, within a company, a well-defined organizational structure acts as the invisible framework that dictates roles, responsibilities, and reporting relationships. This structure, often visualized as a pyramid with distinct levels (tingkatan struktur organisasi perusahaan), ensures smooth operations, efficient communication, and ultimately, the achievement of organizational goals.
But what exactly are these levels, and why are they so crucial for a company's success? Just like a well-oiled machine requires every cog and gear to function in sync, a company relies on each level of its organizational structure to operate efficiently. This article delves into the core of company organizational structures, exploring their significance, types, benefits, and best practices for implementation.
The concept of hierarchical structures within organizations is not new. From ancient military formations to early trade guilds, the need for clear lines of command and defined responsibilities has been recognized for centuries. As businesses evolved, so did the complexity of their structures. The Industrial Revolution, with its emphasis on mass production and specialization, led to the rise of more formalized organizational charts and hierarchies.
The importance of a well-defined organizational structure cannot be overstated. It provides a roadmap for employees, clarifying their roles, responsibilities, and to whom they report. This clarity reduces confusion, streamlines communication, and empowers individuals to make decisions within their designated areas of responsibility. A well-structured organization is also more agile and adaptable to change, as it can quickly adjust roles and responsibilities to meet new challenges and opportunities.
However, structuring an organization is not without its challenges. Balancing the need for control and coordination with the desire for flexibility and autonomy can be tricky. Overly rigid structures can stifle innovation and create bottlenecks, while overly flat structures can lead to confusion and a lack of accountability. Striking the right balance is crucial, and the optimal structure will vary depending on the specific industry, size, and culture of the organization.
While there are many variations, most organizational structures can be broadly categorized into a few common types. Hierarchical structures, often seen in large corporations, feature a clear chain of command with multiple layers of management. Flatter structures, popular among startups and smaller companies, promote greater autonomy and collaboration by minimizing management layers. Matrix structures, common in project-based organizations, allow employees to report to multiple managers based on their roles in different projects. Choosing the right structure is essential for promoting efficiency and achieving organizational goals.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Clear Organizational Structures
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Clear lines of authority and responsibility | Potential for bureaucracy and slow decision-making |
| Improved communication and coordination | Possible limitations on employee creativity and autonomy |
| Increased efficiency and productivity | Difficulty adapting to rapid change or market shifts |
| Enhanced career paths and growth opportunities | Risk of silos and lack of cross-functional collaboration |
By understanding the nuances of organizational structures, companies can create an environment that fosters communication, collaboration, and ultimately, success.
Midsegment of a triangle
Beyond selamat hari raya unpacking the nuance in malay aidilfitri wishes
Navigating the sauk county wisconsin jail system