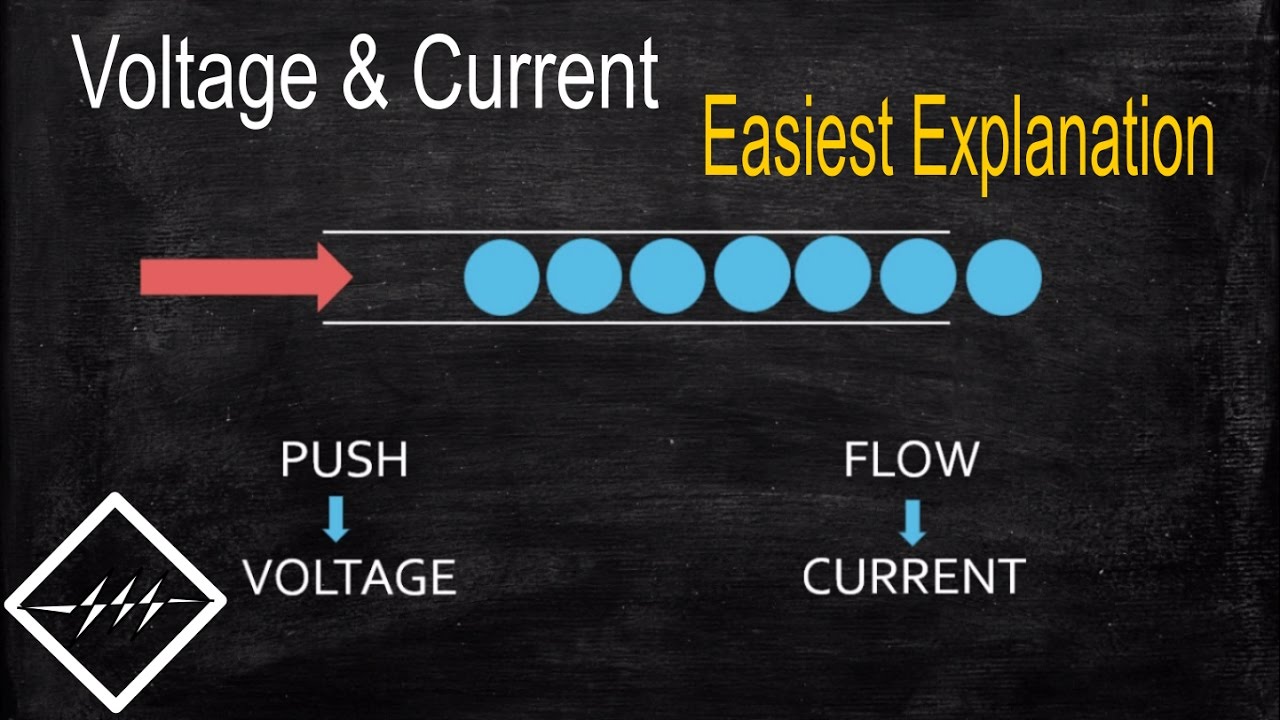
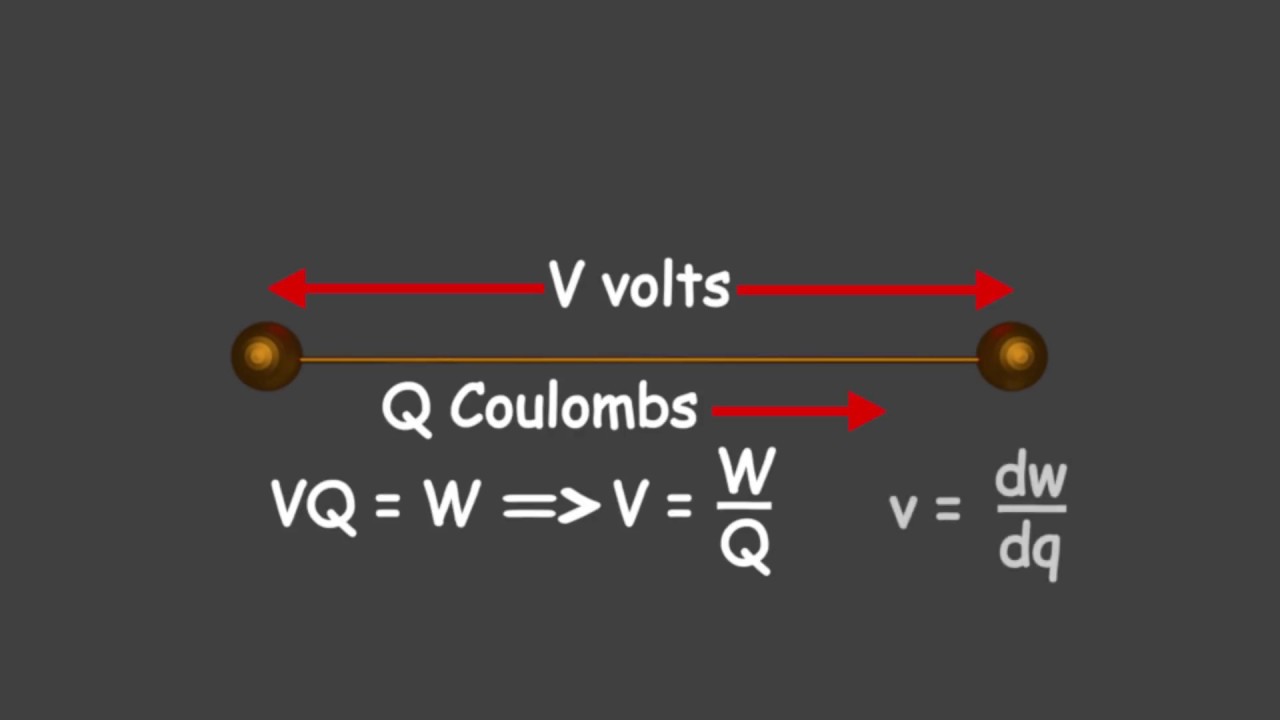
Understanding Voltage The Electric Potential Difference
Ever wonder what makes electricity flow? It's like asking what makes water flow downhill. The answer to the electrical question lies in understanding voltage. It's a fundamental concept that's crucial for grasping how everything from your phone to your refrigerator works. This article will break down what voltage is, its importance, and its practical applications.
So, what is the definition of voltage? Simply put, voltage is the electrical potential difference between two points. It's the "push" or "pressure" that drives electrons through a circuit, much like water pressure pushes water through a pipe. A higher voltage means a greater potential difference and a stronger "push" for the electrons.
Understanding the true meaning of voltage is about more than just a simple definition. It's about grasping the concept of electric potential energy. Think of it like holding a ball above the ground. The higher you hold it, the more potential energy it has. Similarly, a point with a higher voltage has more electrical potential energy than a point with lower voltage.
Voltage meaning becomes clearer when we relate it to its unit of measurement, the volt (V). Named after the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta, the volt quantifies the electric potential difference. A common analogy is to think of voltage as the height of a waterfall. The greater the height, the greater the potential energy of the water at the top, just as a higher voltage represents a greater electrical potential difference.
The history of voltage is intertwined with the discovery of electricity itself. Volta's invention of the voltaic pile, an early battery, marked a significant step in understanding voltage and its role in electrical circuits. This invention laid the foundation for the electrical revolution that transformed our world.
Voltage is the driving force behind all electrical systems. Without voltage, there would be no current flow, and our modern world would be unrecognizable. From powering our homes to running complex industrial machinery, voltage is essential for everything that relies on electricity.
A simple example of voltage in action is a standard AA battery. It typically has a voltage of 1.5 volts. This means there's a potential difference of 1.5 volts between the positive and negative terminals of the battery, which is enough to power small devices like flashlights.
One of the main issues related to voltage is ensuring safety. High voltages can be dangerous and even fatal. Proper insulation, grounding, and adherence to safety regulations are crucial for preventing electrical shocks and accidents.
Benefits of understanding voltage:
1. Troubleshooting electrical problems: Knowing the definition of voltage and how it works helps you diagnose and fix electrical issues in your home or workplace.
2. Selecting the correct electrical equipment: Understanding voltage ratings is crucial for choosing compatible and safe appliances and devices.
3. Designing and building electrical circuits: A deep understanding of voltage is essential for anyone working with electronics or electrical engineering.
Advantages and Disadvantages of High Voltage
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Reduced power loss during transmission | Increased safety risks |
| Smaller conductor sizes can be used | More complex and expensive infrastructure |
Five real examples of voltage:
1. Wall outlet: 120V (North America) or 230V (Europe)
2. Car battery: 12V
3. AA battery: 1.5V
4. High-voltage power lines: Hundreds of kilovolts
5. Lightning strike: Millions of volts
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What is the difference between voltage and current? Voltage is the potential difference, while current is the flow of electric charge.
2. What causes voltage? Voltage is created by various sources, like batteries, generators, and solar cells.
3. What is a voltage drop? Voltage drop is the reduction in voltage across a component in a circuit.
4. How is voltage measured? Voltage is measured using a voltmeter.
5. What is AC voltage? AC voltage (alternating current) periodically changes direction.
6. What is DC voltage? DC voltage (direct current) flows in one direction.
7. What is high voltage? High voltage generally refers to voltages above 600V.
8. What is low voltage? Low voltage typically refers to voltages below 50V.
Tips and tricks related to working with voltage: Always prioritize safety when dealing with electricity. Use insulated tools and wear appropriate safety gear. Consult a qualified electrician for any complex electrical work.
In conclusion, understanding what is the definition of voltage is fundamental to our interaction with the modern world. From the simplest battery-powered device to the complex power grid that lights our cities, voltage is the driving force behind it all. It's a concept with a rich history, significant importance, and a direct impact on our daily lives. Learning about voltage empowers us to troubleshoot problems, make informed decisions about electrical equipment, and appreciate the intricate workings of the electrical systems that surround us. By grasping this crucial concept, we can better navigate the electrified world we live in and appreciate the marvel of this invisible force that powers our lives. Start exploring the world of voltage today, and you'll unlock a deeper understanding of the technology that shapes our modern existence. It's not just about definitions, it's about understanding the power that drives our world.
Unlock your cars worth determining vehicle value with vin
Elevate your watersports the ultimate guide to boat ski tow pylons
The enduring appeal of font old english script


/GettyImages-603713295-59ab1d639abed50011ef7774.jpg)