Navigating Stair Safety: Understanding Handrail Codes
Have you ever paused mid-staircase, hand grasping for a sturdy rail, and felt a surge of gratitude for its presence? While seemingly simple, stair handrails are crucial safety features governed by specific codes and regulations. Understanding these guidelines isn’t just for architects and builders; it's about ensuring safe and accessible environments for everyone.
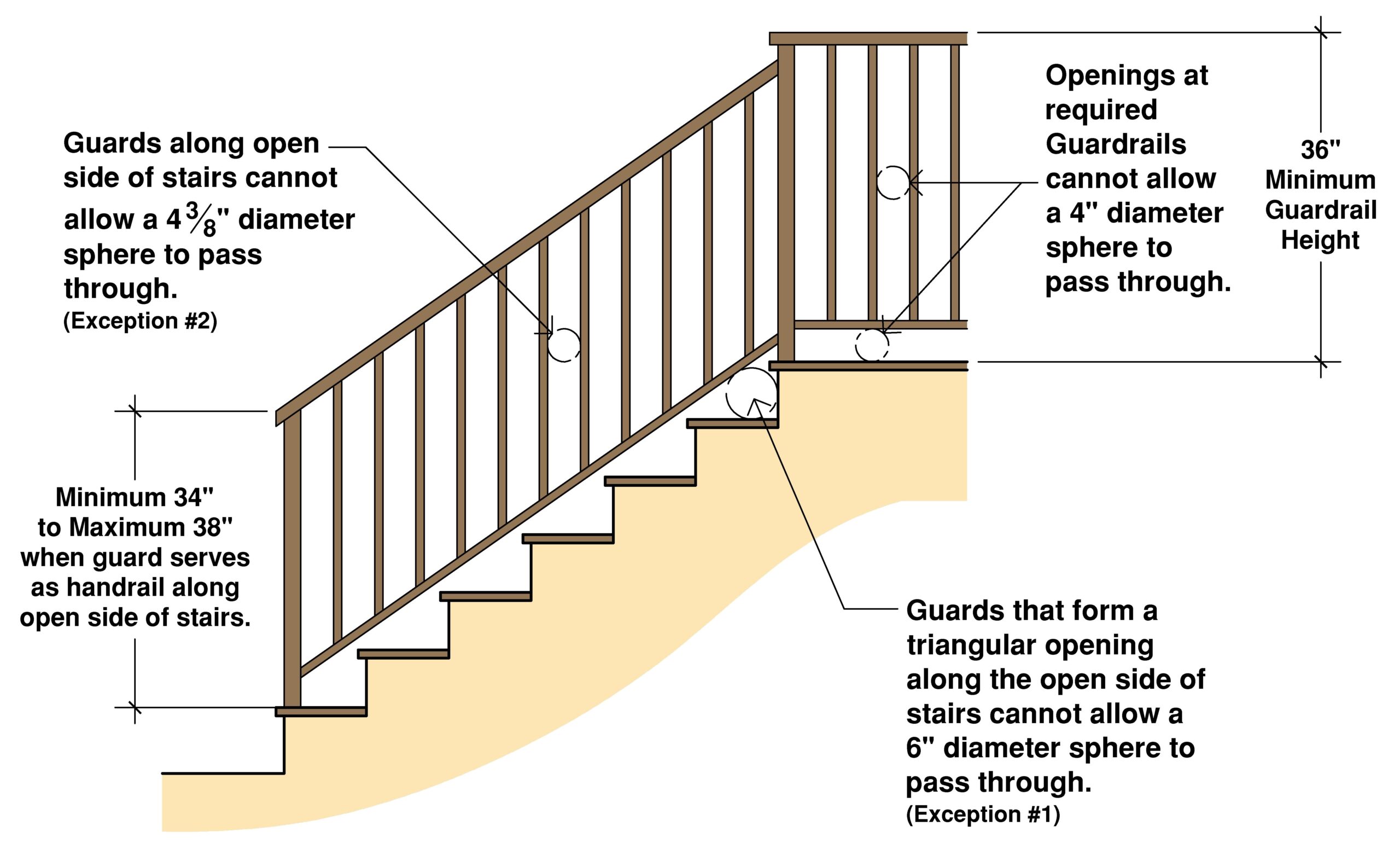
Stair handrail codes, often incorporated into building regulations, provide specific requirements for the design, installation, and maintenance of handrails. These regulations address aspects like height, material, continuity, and structural integrity. They aim to minimize the risk of falls, offering support and stability to individuals navigating stairs.
Historically, stair handrail regulations evolved alongside construction practices and an increased awareness of safety. Early building codes may have lacked specific handrail provisions. However, as construction techniques advanced and accident prevention became a priority, the need for standardized guidelines became apparent. The codification of handrail regulations, therefore, represents a commitment to public safety and accessibility.
The importance of adhering to stair handrail codes cannot be overstated. These regulations provide a framework for safe and inclusive design, mitigating the risk of falls and injuries, particularly among children, the elderly, and individuals with mobility challenges. They also ensure consistency in design and construction, contributing to the overall structural integrity of buildings.
One of the primary issues surrounding stair handrail codes is ensuring compliance. Keeping up with evolving regulations, interpreting complex guidelines, and addressing unique site conditions can be challenging. However, overcoming these challenges is essential to fostering safe and accessible environments.
Benefits of adhering to stair handrail codes are numerous. Enhanced safety is paramount, reducing the risk of falls and promoting user confidence. Improved accessibility is another key advantage, ensuring that individuals of all abilities can navigate stairs safely and independently. Furthermore, compliance with regulations demonstrates a commitment to responsible building practices and can contribute to increased property value.
Developing an action plan for implementing stair handrail code compliance involves several steps. Begin by researching local and national building codes. Consult with architects, engineers, and contractors to ensure proper design and installation. Regularly inspect and maintain handrails to address any wear and tear or damage.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Strict Handrail Code Adherence
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Increased Safety | Potentially Higher Initial Costs |
| Improved Accessibility | Increased Design Complexity in Certain Cases |
| Code Compliance | Potential for Over-Engineering in Some Scenarios |
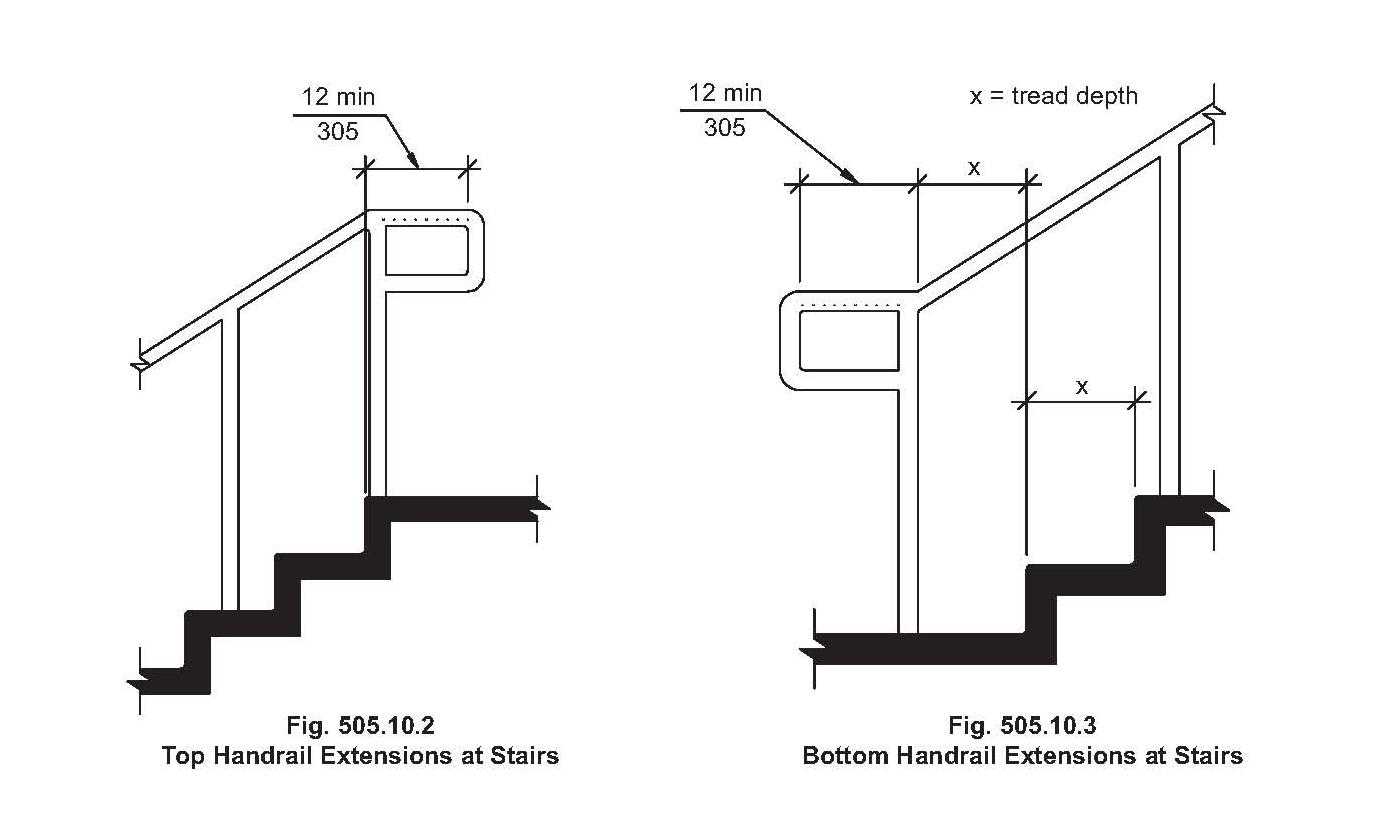
Best practices for implementing stair handrail codes include: ensuring continuous handrails along the entire length of the staircase; using materials that provide a firm grip; installing handrails at the appropriate height; securely anchoring handrails to the wall or supporting structure; and conducting regular inspections to ensure ongoing compliance.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What is the standard height for a handrail? (Answer: Regulations vary, but a common range is 34-38 inches.)
2. What materials are acceptable for handrails? (Answer: Wood, metal, and composite materials are common.)
3. Do all staircases require handrails? (Answer: Building codes typically mandate handrails for staircases with a certain number of risers.)
4. What is the purpose of a handrail return? (Answer: To prevent clothing snags and provide a continuous grip.)
5. How often should handrails be inspected? (Answer: Regularly, ideally as part of a broader building maintenance schedule.)
6. Are there different handrail requirements for residential and commercial buildings? (Answer: Yes, regulations can vary based on building occupancy and use.)
7. Where can I find information about local handrail codes? (Answer: Contact your local building department or access online resources.)
8. What are some common handrail code violations? (Answer: Incorrect height, inadequate graspability, lack of continuity.)
Tips and tricks for navigating handrail code compliance include staying informed about updates to building regulations, consulting with experienced professionals, and documenting all inspection and maintenance activities.
In conclusion, stair handrail codes play a vital role in ensuring safety and accessibility in built environments. From providing stability to preventing falls, these regulations contribute to a more inclusive and secure world for everyone. Understanding and adhering to these guidelines is not merely a matter of compliance; it's a commitment to creating spaces where individuals can navigate with confidence and peace of mind. By prioritizing handrail safety, we contribute to a more accessible and inclusive world for all. Take the time to familiarize yourself with local regulations and best practices. Your efforts can make a significant difference in preventing accidents and promoting a safer environment for yourself and others.
Navigating the idaho correctional system a guide
Unlocking the magic a deep dive into under the oak tree on mangastic
Duramax diesel troubles navigating common issues









:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/stair-handrail-and-guard-code-1822015-FINAL1-5c054b4dc9e77c0001600219.png)


