Decoding the UK's Electrical Wiring Colour Code: Black, Brown, and Grey
Navigating the world of electrical wiring can be daunting, especially with the varied colour codes used in different countries. In the UK, the colours black, brown, and grey play crucial roles in identifying the functions of wires within electrical circuits. This article will delve into the meaning and importance of these colours, providing a comprehensive guide for anyone working with UK electrical systems.
Understanding the UK wiring colour code is essential for safety and proper functionality. Whether you're a DIY enthusiast undertaking a home improvement project or a seasoned electrician, knowing the purpose of each wire is paramount. Misinterpreting the colour code can lead to dangerous situations, including electric shocks, short circuits, and even fires. Therefore, a solid understanding of the black, brown, and grey wire designations is critical.
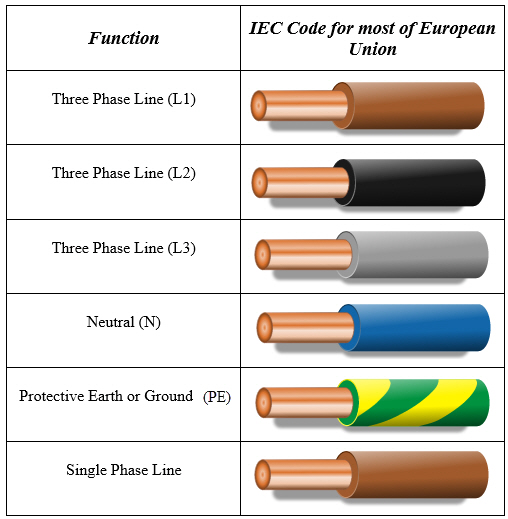
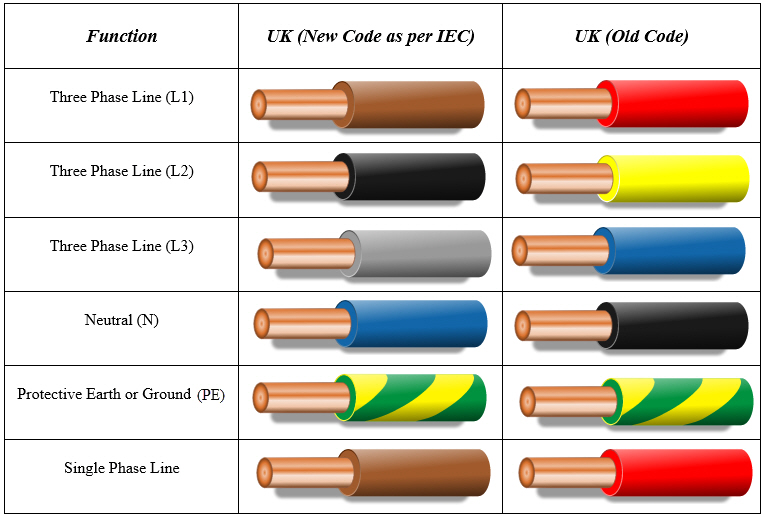
Historically, the UK has seen changes in its wiring colour codes. The current system, incorporating brown, blue, and green/yellow for live, neutral, and earth respectively, replaced the older red, black, and green system. The colours black and grey are often found in older installations or in specific applications. Black typically represented the neutral wire in older systems, while grey has been used for switched live wires in lighting circuits.
The significance of correctly identifying these wires cannot be overstated. Connecting wires incorrectly based on a misinterpretation of the colour code can have dire consequences. For instance, connecting a live wire to a neutral terminal can create a short circuit, potentially damaging appliances and posing a fire hazard. Similarly, confusing the earth wire with a live or neutral wire can compromise safety and lead to electric shocks.
In contemporary UK wiring regulations, black is primarily used for the neutral wire in certain situations, such as switch lines. Grey, on the other hand, is frequently employed as a switched live wire, particularly in lighting circuits. Understanding these distinctions is vital for anyone undertaking electrical work, whether it's installing a new light fixture or troubleshooting an existing circuit.
One benefit of using distinct colours is easy identification. This simplifies circuit tracing and fault finding. Another advantage is the enhanced safety provided by a standardized colour code. Consistent use minimizes the risk of misconnections and subsequent hazards. Finally, a clear understanding of the colour code facilitates effective communication between electricians and other professionals working on electrical installations.
When dealing with older wiring, it’s crucial to verify the function of each wire with a voltage tester rather than relying solely on colour. Always isolate the power supply before working on any electrical circuits. If you are unsure about any aspect of electrical work, consult a qualified electrician.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Standardized Wiring Colours
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Safety | Confusion with older systems |
| Simplified Troubleshooting | Potential for misidentification if insulation is damaged |
| Improved Communication |
Best Practices:
1. Always isolate the power supply before working on electrical circuits.
2. Use a voltage tester to confirm the function of each wire.
3. Consult the latest wiring regulations for specific applications.
4. Never assume the colour code without verification, especially in older installations.
5. If in doubt, consult a qualified electrician.
FAQs:
1. What does a black wire typically represent in older UK wiring systems? (Neutral)
2. What is the common function of a grey wire in UK wiring? (Switched Live)
3. Why is it important to verify wire function with a tester? (Colours can fade or be misidentified)
4. What are the current standard colours for live, neutral, and earth in the UK? (Brown, Blue, Green/Yellow)
5. When should I consult a qualified electrician? (When unsure about any aspect of electrical work)
6. Can grey wires be used for other functions besides switched live? (Yes, in specific circumstances but less common)
7. Are there any online resources for understanding UK wiring colours? (Yes, several websites and forums provide information)
8. What precautions should I take when working with older wiring? (Always isolate the power and verify wire functions with a tester)
Tips and Tricks: Label wires clearly after identification to avoid future confusion. Use appropriate wire connectors and ensure secure connections. Maintain a tidy wiring layout for easier troubleshooting.
In conclusion, understanding the significance of black, brown, and grey wires in UK electrical wiring is paramount for safety and proper circuit functionality. While these colours may represent different functions depending on the age and type of installation, adhering to best practices, utilizing proper testing methods, and consulting reliable resources ensures correct identification and safe operation. The standardization of wiring colours significantly enhances safety, simplifies troubleshooting, and improves communication among professionals. However, it’s crucial to be aware of potential confusion with older wiring systems and always verify wire function with a tester. By prioritizing safety and accurate identification, you can confidently navigate the complexities of UK electrical wiring and complete projects efficiently and safely. Remember, if any doubts arise, consulting a qualified electrician is always the best course of action to guarantee your safety and the integrity of your electrical systems. This will prevent potential hazards and ensure long-term reliability.
Gacha life bases with hair your avatars crowning glory
Ace your california dmv test driver handbook pdf guide
Pastel decorations for childrens day celebrations




/ElectricalWiring_FINAL2-5c01dc0546e0fb0001f4d760.png)