Decoding the GS 12 Salary: Your Comprehensive Guide
Navigating the federal government's General Schedule (GS) pay system can feel like traversing a complex maze. For those eyeing or currently holding a GS 12 position, understanding the intricacies of the GS 12 salary structure is paramount. This comprehensive guide breaks down everything you need to know about GS 12 compensation, from base salary to locality adjustments and beyond.
The GS 12 level represents a significant step in a federal career, often signifying managerial or high-level specialist roles. Consequently, the GS 12 salary reflects this increased responsibility and expertise. But what exactly does a GS 12 employee earn? The answer isn't straightforward. Several factors influence the final compensation figure, making it crucial to understand the nuances of the GS pay system.
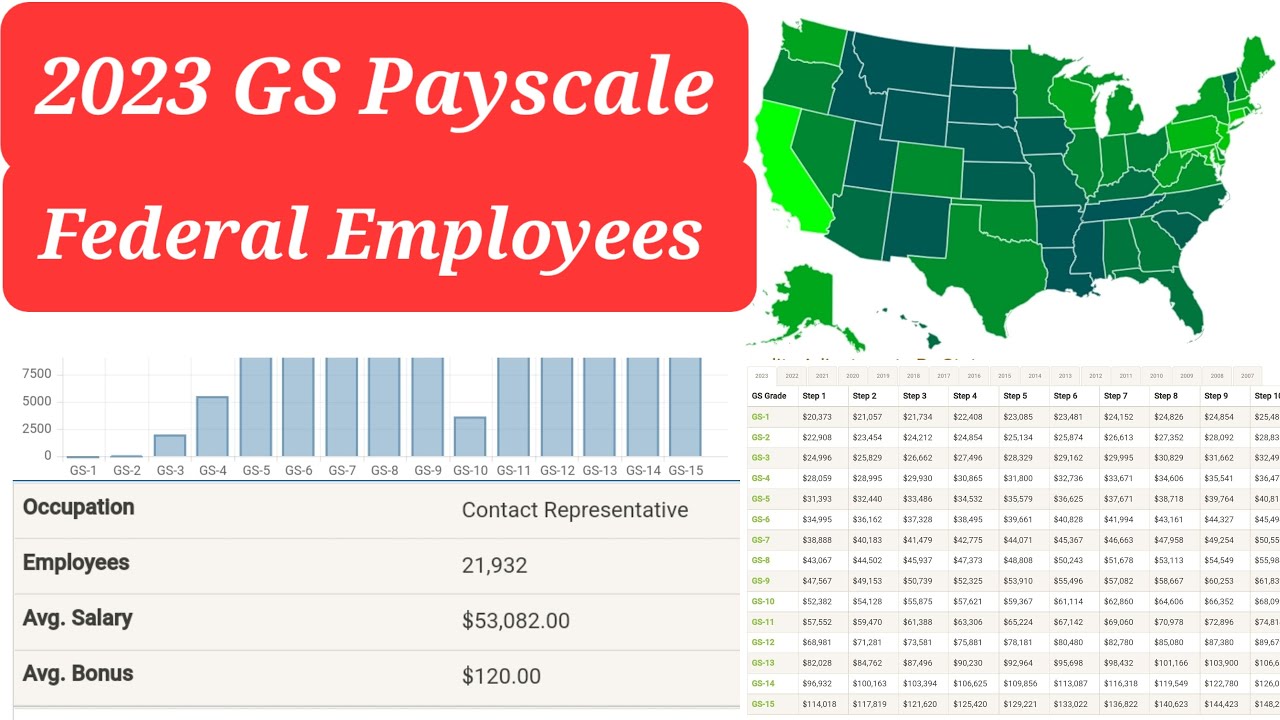
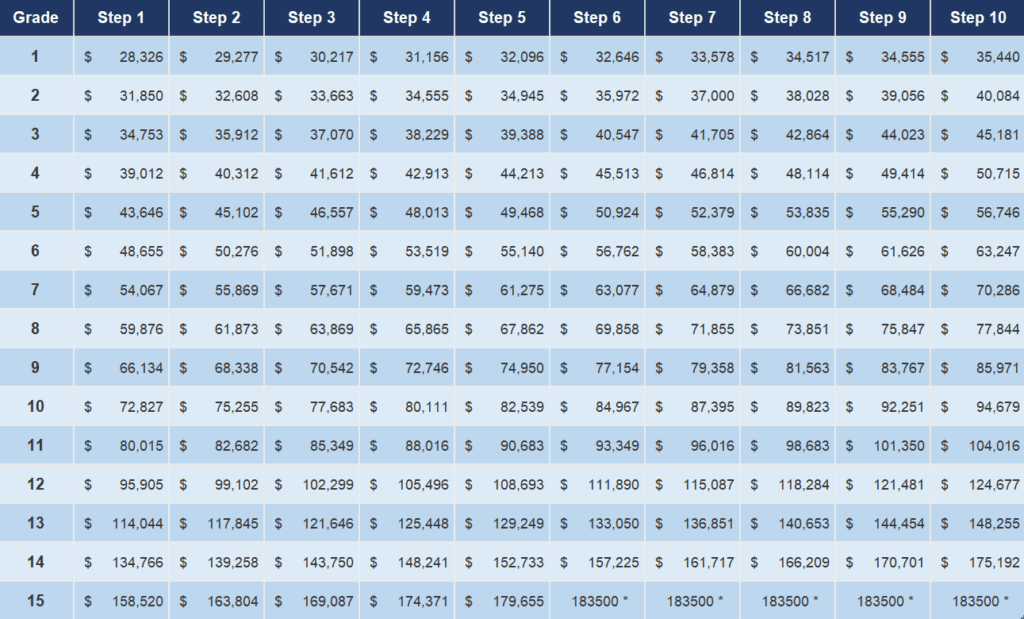
The foundation of the GS 12 compensation package is the base salary, which is established annually by the Office of Personnel Management (OPM). This base salary is further adjusted based on geographic location, acknowledging the varying cost of living across the United States. This crucial element, known as locality pay, ensures that federal employees maintain a comparable standard of living regardless of their duty station.
Beyond base salary and locality pay, the GS 12 compensation picture includes other potential elements such as within-grade increases (WGIs), based on performance and tenure, and potential bonuses or awards for exceptional contributions. Understanding these components allows GS 12 employees to maximize their earning potential and plan for their financial future.
Historically, the GS pay system was designed to create a standardized and fair compensation structure across the federal government. This system aimed to eliminate pay disparities based on factors unrelated to job performance and experience. The GS 12 level, within this structure, signifies a high level of professional achievement and carries with it a corresponding salary expectation.
One of the main issues surrounding the GS pay scale, including the GS 12 level, is maintaining its competitiveness with the private sector. Ensuring that federal salaries attract and retain top talent remains a constant challenge. Another key concern is the transparency and understandability of the system itself. Navigating the complexities of base pay, locality adjustments, and other factors can be daunting for even seasoned federal employees.
A GS 12 employee's salary is calculated using the base GS pay table published by OPM and adjusted by the specific locality pay percentage for their geographic area. For example, a GS 12, Step 1 employee in New York City with a higher locality pay adjustment will earn more than a GS 12, Step 1 employee in a lower-cost area.
Benefits of the structured GS 12 pay scale include: Predictability (clear salary progression based on steps and grades), Fairness (standardized pay across agencies), and Competitive compensation designed to attract qualified professionals.
Advantages and Disadvantages of the GS 12 Pay Scale
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Clear career progression | Limited negotiation flexibility |
| Stable employment | Salary compression at higher levels |
| Comprehensive benefits package | Potential for slower salary growth than private sector |
Best Practices: 1. Understand your locality pay. 2. Plan for within-grade increases. 3. Explore potential bonuses. 4. Review the annual OPM pay tables. 5. Utilize online GS pay calculators.
Frequently Asked Questions: 1. How is locality pay calculated? 2. What is a within-grade increase? 3. How often does the GS pay scale change? 4. Are there opportunities for bonuses at the GS 12 level? 5. How does the GS 12 salary compare to the private sector? 6. What is the highest step for a GS 12? 7. How can I advance beyond GS 12? 8. Where can I find the official GS pay tables?
Tips and Tricks: Utilize online resources like the OPM website for the most up-to-date salary information. Consult with your agency's human resources department for specific guidance on pay and benefits.
In conclusion, understanding the GS 12 pay scale is essential for anyone pursuing or currently in a GS 12 position. This structured compensation system, with its base salary, locality adjustments, and potential for additional earnings, provides a framework for career progression and financial planning. While navigating the complexities of the GS system can be challenging, the benefits of a clear and predictable salary structure, combined with the potential for career advancement within the federal government, make it a rewarding path for many professionals. Take the time to research, understand your specific situation, and leverage the available resources to maximize your earning potential and achieve your career goals within the GS system. The GS 12 level represents a significant achievement, and a thorough understanding of the accompanying pay scale is crucial for making informed decisions and planning for a successful future. Don't hesitate to consult official resources and seek guidance from HR professionals to navigate this complex landscape effectively.
Navigating medicare supplement insurance understanding aarp medicare part f plans
Echoes of change the enduring power of female folk singers of the 50s 60s
Navigating arkansas food assistance your ebt application guide