Decoding Air Pump Heating: How It Works and Why It Matters
So, you're curious about air pump heating? Join the club. These systems, increasingly popular for their energy efficiency, might seem like magic, but they’re based on some pretty clever thermodynamic principles. This isn’t your grandpa's furnace. Let's dive into the fascinating world of air pump heating and discover how these systems can keep you toasty while being kinder to your wallet and the environment.
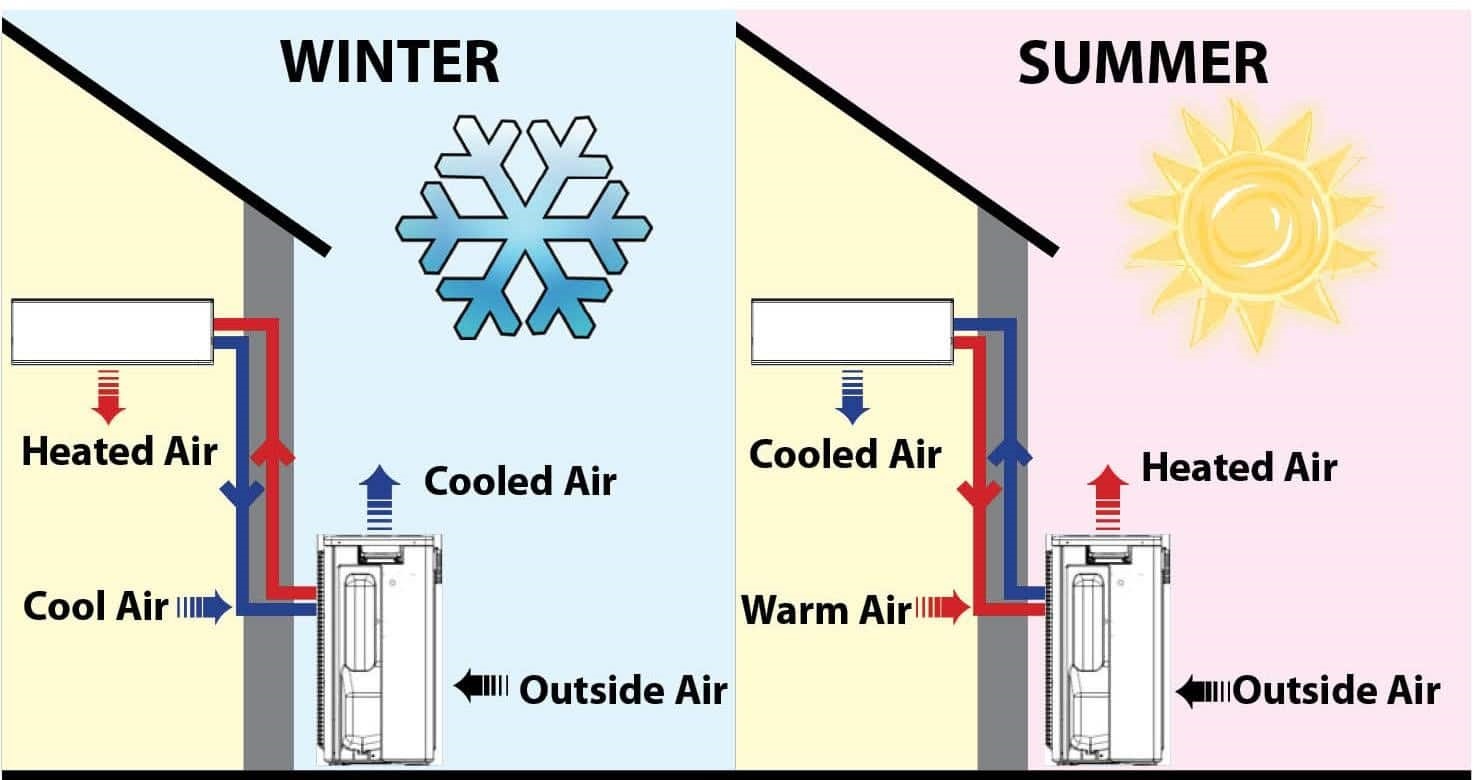
Air pump heating, more accurately known as air-source heat pump heating, is becoming a serious contender in the world of home climate control. But how exactly does an air pump heating system function? Essentially, it's a refrigerator in reverse. Instead of cooling your food, it extracts heat from the outside air and transfers it inside to warm your home. Yes, even on chilly days, there's heat energy in the air, and these systems are designed to capture it.
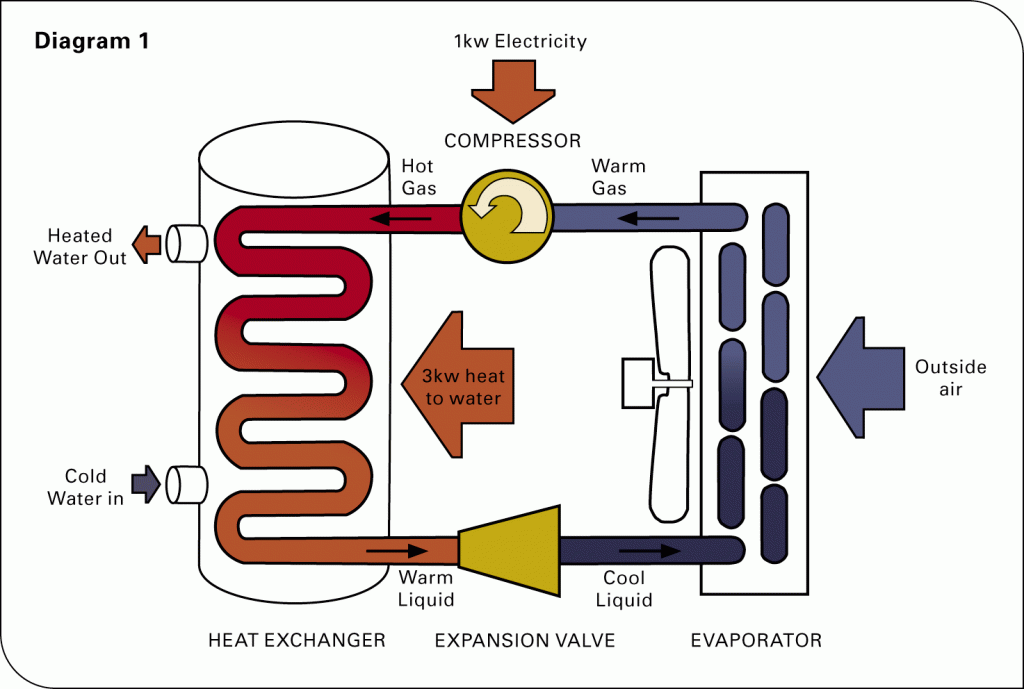
The core concept behind the functionality of an air-source heat pump revolves around a refrigerant that circulates through a closed loop system. This refrigerant absorbs heat from the outside air, even in cold temperatures. As the refrigerant absorbs heat, it changes from a liquid to a gas. This gas is then compressed, raising its temperature even further. The heated gas then passes through a heat exchanger inside your home, releasing its heat and warming your indoor air. The refrigerant then cools, condenses back into a liquid, and the cycle begins anew.
While the concept of using outside air for heating might seem relatively new, the underlying principles have been around for a while. Early forms of heat pump technology date back to the mid-19th century, but it wasn't until the latter half of the 20th century that air-source heat pumps became commercially viable for residential heating. Their rising popularity is largely driven by increasing energy costs and growing environmental concerns. These systems can significantly reduce energy consumption compared to traditional heating methods, making them an attractive option for homeowners seeking both comfort and cost savings.
A major issue surrounding the discourse on how an air pump heating system operates is the misconception that they can’t work in cold climates. While their efficiency does decrease as the outside temperature drops, modern air-source heat pumps are designed to operate effectively even in sub-zero temperatures. Advancements in technology, like variable-speed compressors and improved refrigerants, have significantly enhanced their cold-weather performance. Understanding how these systems function in different weather conditions is crucial for maximizing their effectiveness.
One of the biggest advantages of an air pump heating system is its energy efficiency. They can deliver up to three times the amount of heat energy for the same amount of electricity compared to electric resistance heating. This translates to lower energy bills and a smaller carbon footprint. Another benefit is their versatility. Many air-source heat pumps can also provide cooling in the summer, functioning as an air conditioner and eliminating the need for a separate cooling system. Furthermore, these systems require less maintenance than traditional heating systems, reducing the need for frequent servicing.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Air Pump Heating Systems
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | Lower efficiency in extreme cold |
| Heating and Cooling Capability | Higher upfront cost |
| Lower Maintenance | Potential for noise |
Best Practices for Implementing Air Pump Heating:
1. Proper Sizing: Ensure the system is correctly sized for your home's heating needs.
2. Professional Installation: Hire a qualified HVAC technician for installation.
3. Regular Maintenance: Schedule annual maintenance checks.
4. Proper Insulation: Ensure your home is well-insulated to maximize efficiency.
5. Thermostat Control: Utilize programmable thermostats for optimal control.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. Can air source heat pumps work in cold climates? Yes, even in sub-zero temperatures.
2. Are they expensive to install? Higher upfront cost, but long-term savings.
3. Do they require a lot of maintenance? Generally less than traditional systems.
4. How long do they last? Typically 15-20 years with proper maintenance.
5. Are they noisy? Modern systems are designed to be quiet.
6. Can they also cool my home? Many models offer both heating and cooling.
7. What is the average cost of operation? Lower than electric resistance heating.
8. Are there government incentives for installing them? Often rebates and tax credits are available.
In conclusion, understanding how an air pump heating system works is essential for anyone considering a more efficient and environmentally friendly way to heat their home. From their ability to extract heat from even cold air to their dual functionality as both a heating and cooling system, air-source heat pumps offer a compelling alternative to traditional heating methods. While the initial investment may be higher, the long-term energy savings, reduced environmental impact, and increased comfort make them a worthwhile investment. If you're looking for a way to stay warm and cozy while saving money and reducing your carbon footprint, exploring air-source heat pump technology is definitely worth your time. Take the leap and discover the future of home heating today.
Navigating grief resthaven funeral home and cremation services disrupted
Fernsehprogramm heute abend ndr 3
The allure of anime boy in hoodie on building