Deciphering the P0157 Code: Oxygen Sensor Insights for Smoother Drives
Is your car's check engine light glaring at you? A common culprit behind this ominous glow is the dreaded diagnostic trouble code (DTC) P0157. This cryptic code can leave drivers feeling lost and confused. But fear not, understanding what this code signifies is the first step towards a solution and a smoother, more efficient ride.
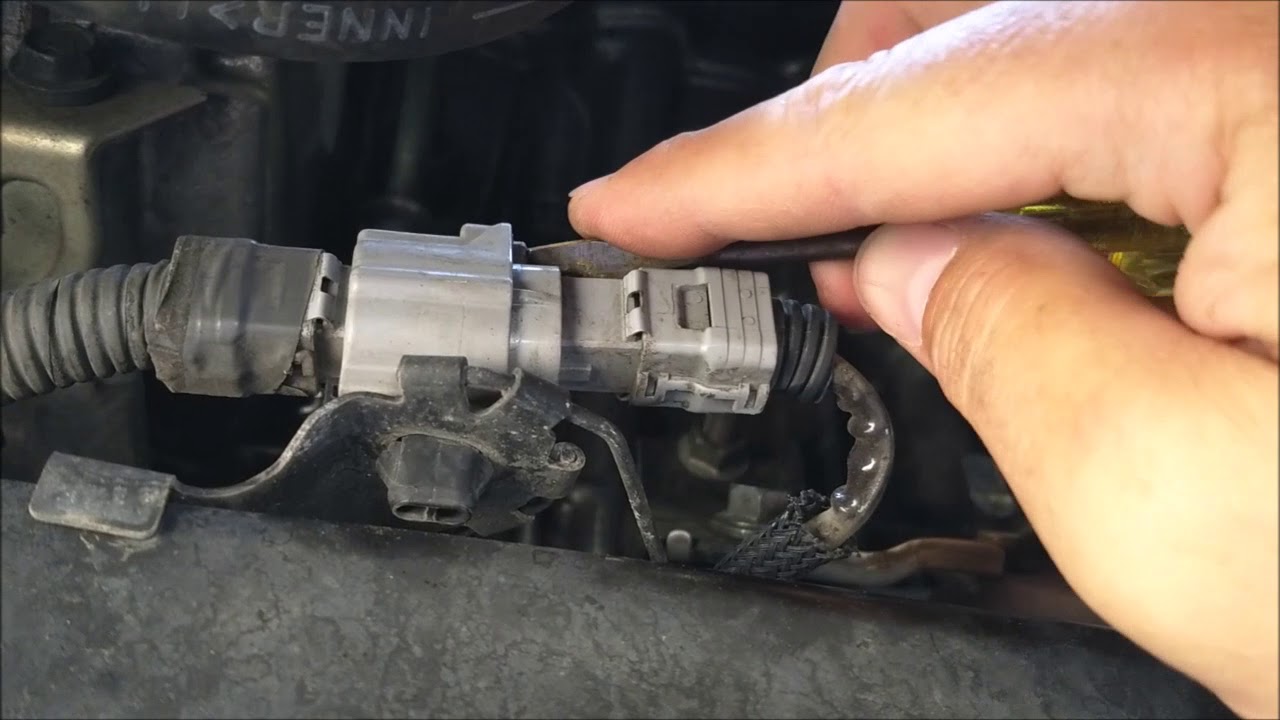
The P0157 code specifically points to a problem with the oxygen sensor downstream of the catalytic converter on Bank 2 (the side of the engine that doesn't contain cylinder #1). This sensor, often called the O2 sensor, plays a crucial role in monitoring the exhaust gases leaving your engine. This information allows the engine control unit (ECU) to fine-tune the air-fuel mixture, optimizing performance and minimizing emissions.
A P0157 code indicates that the voltage signal from this specific oxygen sensor is reading low for an extended period. This low voltage suggests an excessive amount of oxygen in the exhaust, hinting at a lean fuel mixture or a potential issue with the sensor itself. Ignoring this code could lead to decreased fuel economy, increased emissions, and potentially even damage to the catalytic converter.
While the exact origin of standardized OBD-II codes like P0157 isn't tied to a specific inventor or event, their importance lies in creating a universal language for vehicle diagnostics. Before standardized codes, deciphering engine problems was a much more complex and time-consuming process. These codes paved the way for more accessible and efficient troubleshooting.
The P0157 code isn't just about a faulty sensor; it's about understanding the complex interplay of components within your vehicle's emission control system. The downstream oxygen sensor's primary function is to monitor the effectiveness of the catalytic converter. Therefore, a low voltage signal could indicate a problem with the converter itself, although this is less common than a sensor issue.
A common cause of the P0157 code is a malfunctioning oxygen sensor. Other potential culprits include exhaust leaks, vacuum leaks, a faulty fuel injector, low fuel pressure, or even a wiring issue. A proper diagnosis involves checking for these related problems to pinpoint the root cause.
One benefit of having diagnostic codes like P0157 is the ability to quickly identify potential issues. This saves time and money compared to the older, more trial-and-error methods of diagnostics. Another benefit is the improved ability to address emissions concerns, leading to a cleaner environment. Lastly, understanding these codes empowers car owners to make informed decisions about repairs, avoiding unnecessary expenses.
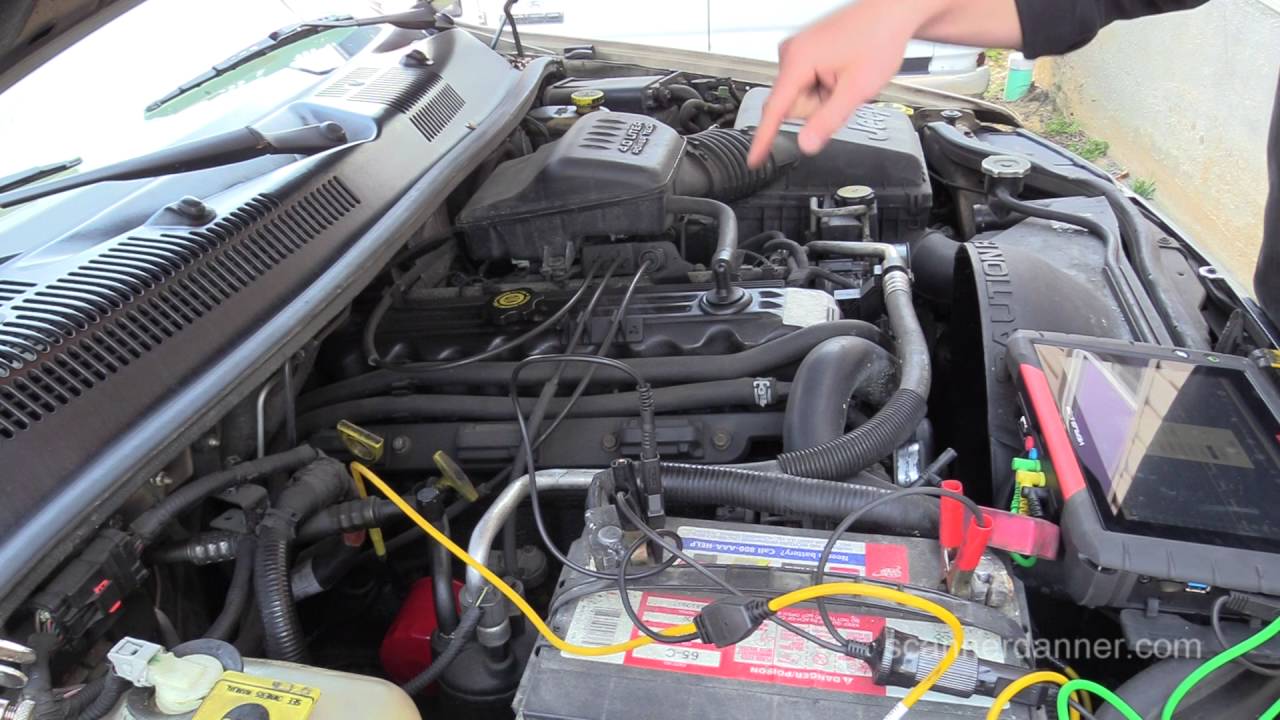
Troubleshooting a P0157 code typically involves visually inspecting the oxygen sensor and its wiring for damage, checking for exhaust leaks, and using a diagnostic scanner to monitor sensor readings. Replacing the oxygen sensor is often the first step, but a thorough diagnosis is essential to avoid replacing parts unnecessarily.
Advantages and Disadvantages of OBD-II Codes like P0157
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Quick identification of potential issues. | Can sometimes be misleading without proper diagnostic procedures. |
| Facilitates easier communication between mechanics and car owners. | Requires specialized tools and knowledge for accurate interpretation. |
Five best practices for addressing a P0157 code include: 1) Consult a reliable repair manual or online resource, 2) Use a high-quality diagnostic scanner, 3) Inspect related components like the exhaust system and fuel injectors, 4) Replace the oxygen sensor with an OEM or equivalent part, 5) Clear the code and monitor for recurrence.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What is a P0157 code? - It indicates a low voltage reading from the downstream oxygen sensor on Bank 2.
2. What causes a P0157 code? - A faulty sensor, exhaust leaks, or fuel system problems.
3. Can I drive with a P0157 code? - While possible, it's not recommended as it can impact fuel economy and potentially damage the catalytic converter.
4. How much does it cost to fix a P0157 code? - Costs vary depending on the underlying cause, but sensor replacement is typically a few hundred dollars.
5. How do I fix a P0157 code? - Diagnose the root cause and replace any faulty components.
6. What tools do I need to diagnose a P0157 code? - A diagnostic scanner is essential.
7. Is a P0157 code serious? - While not immediately critical, it should be addressed to prevent further issues.
8. Can I fix a P0157 code myself? - With some mechanical aptitude and the right tools, it's possible.
Tips and tricks: Always disconnect the battery before working on any electrical components. Use a penetrating oil to loosen stubborn oxygen sensors. Consult a repair manual specific to your vehicle make and model.
Understanding and addressing diagnostic trouble codes like P0157 is crucial for maintaining your vehicle's health and performance. While encountering these codes can be frustrating, they provide valuable insights into the inner workings of your car. By recognizing the importance of these codes and taking appropriate action, you can ensure a smoother, more efficient, and ultimately more enjoyable driving experience. Don't let a cryptic code like P0157 intimidate you. Empower yourself with knowledge, take the necessary steps for diagnosis and repair, and get back on the road with confidence.
Signing power navigating letters of authorization
Doubletree 611 nw loop 410 san antonio
Unlocking elk river mn your guide to zoning regulations